Fast checkout
With Fast checkout you can offer your customers a seamless, one-click checkout experience by automatically collecting their shipping address and delivery method during the checkout process.
This way, your application can skip the shipping flow, which requires users to manually enter their shipping details during checkout and the customer can use existing shipping details stored by Revolut Pay.
This tutorial assumes you are familiar with a standard implementation of Revolut Pay. For more information, see:
How to implement Fast checkout
Complete the following steps to integrate the Fast checkout flow in your Revolut Pay implementation:
- Set up webhook for address validation
- Set up your backend to respond to address validation requests
- Initialize Revolut Pay widget with Fast checkout
Manage multiple stores with Fast checkout
Optionally, you can register multiple storefronts to use with Fast checkout. The Locations API allows you to manage multiple online stores. Registering locations lets you differentiate and group your orders from different stores. You can also introduce custom processes for your orders on each location.
For example, you can run different address validations or have different shipping price applied on each location.
How to set up multiple stores
To set up multiple stores with Fast checkout, follow and repeat these steps for each location:
- Register an online location using the Create a location endpoint.
- Register address validation endpoint with the
location_idparameter pointing to the registered location.
For more information about this step, see: Set up webhook for address validation
- Configure your custom processes on your backend for each registered location (e.g., address validation, custom pricing, etc.).
For more information about address validation for Fast checkout, see: Set up your backend to respond to address validation requests
- Send the
location_idparameter in the request body during order creation to assign the order to a specific location.
1. Set up webhook for address validation
Revolut Pay manages the user's shipping address(es) and during checkout the user's preferred shipping address will be sent to your backend for validation.
To set up your endpoint to receive addresses, you must use the /synchronous-webhooks endpoint.
Take into consideration your implementation environment:
- For implementation in Production environment, use:
https://merchant.revolut.com/api/synchronous-webhooksand your Production API Secret key in the request header. - For implementation in Sandbox environment, use:
https://sandbox-merchant.revolut.com/api/synchronous-webhooksand your Sandbox API Secret key in the request header.
Send a request with the following body to the /synchronous-webhooks endpoint:
{
"event_type": "fast_checkout.validate_address",
"url": "<yourEndpointUrl>"
}
Where url is a valid URL pointing to an endpoint on your backend that will handle incoming HTTPS POST requests from Revolut Pay.
This call registers the endpoint you provided that will receive shipping addresses for validation.
You only need to register your endpoint URL once. Multiple calls to the /synchronous-webhooks endpoint will override the previously registered URL and signing_key.
Example response
The following JSON object is returned after registering your endpoint:
{
"id": "5c08dcc1-cd60-4b7d-a255-e42d24d7365c",
"signing_key": "swsk_VsuFcq6FIpa9gOWUu0n2WxiCbsDHIJlN",
"url": "<yourEndpointUrl>",
"event_type": "fast_checkout.validate_address"
}
The signing key will be used by Revolut to compute a Hash-based Message Authentication Code (HMAC) payload signature whenever the registered URL is called. The calculated HMAC code is sent in the header (Revolut-Pay-Payload-Signature) of address validation requests, which should be verified by your backend. For more information, see: Merchant API: Payload Signature.
2. Set up your backend to respond to address validation requests
After you registered your address validation URL successfully, you have to handle address validation requests on your backend. To do this follow these steps.
(Optional) 2.1. Validate the signing key
When Revolut sends you a shipping address for validation, the request payload is signed and the Revolut-Pay-Payload-Signature HTTP header contains the HMAC calculated using the signing_key. You can validate the payload by computing the HMAC using the signing_key and comparing your HMAC to the received. For more information, see: Merchant API: Payload Signature.
2.2. Validate the address and get delivery methods
When you receive an address from Revolut, it is important to make sure the address meets the following criteria:
- Address is valid and can be stored in your database
- You (or your shipping partner) can deliver to the address
Once you know the address is valid, you can either fetch available delivery methods from your database, or retrieve them from you shipping partner.
The body of address validation requests has the following JSON structure:
{
order_id: String,
shipping_address: {
street_line_1: String,
street_line_2: String,
region: String,
city: String,
country_code: String,
postcode: String
},
metadata: Object
}
Address validation object:
| Parameter | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|
order_id | ID of order where shipping address needs validation. | String |
shipping_address | An object containing the shipping address to be validated. | Object |
metadata | Order metadata fields (retrieved from order.metadata object) that can be validated during address validation, including the merchant_order_ext_ref. | Object |
Shipping address object:
| Parameter | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|
street_line_1 | Street line 1 information. | String |
street_line_2 | Street line 2 information. | String |
region | The region associated with the address. | String |
city | The city associated with the address. | String |
country_code | The country associated with the address. | String |
postcode | The postcode associated with the address. | String |
2.3. Respond to the synchronous webhook call
After running the validation on the retrieved shipping address, your backend should respond with a JSON object containing the result of validation, using the following structure:
{
valid: Boolean,
delivery_methods: [
{
ref: String,
amount: Number,
label: String,
description: String
}
]
}
If the address is invalid (either based on your or your shipping partner's validation), or there are no delivery methods available return the following JSON object:
{
valid: false,
delivery_methods: []
}
More details on the validation object:
| Parameter | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|
valid | Indicates whether delivery is possible to the retrieved shipping address.
| Boolean |
delivery_methods | A list of objects containing information about the available delivery methods. | List of objects |
Delivery methods object:
| Parameter | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|
ref | A reference ID to identify the delivery method. | String, max. 100 characters |
amount | The cost of the delivery method (minor currency unit). For example, 1999 for $19.99.caution The currency of the delivery cost displayed is based on the currency of the order. If your shipping partner uses another currency to determine the delivery cost, conversion should be made. | Number |
label | The display name of the delivery method. | String, max. 100 characters |
description | (Optional) A short description of the delivery method. | String, max. 1024 characters |
Displaying delivery methods on the widget
This is how available delivery methods are displayed on the Revolut Pay widget:
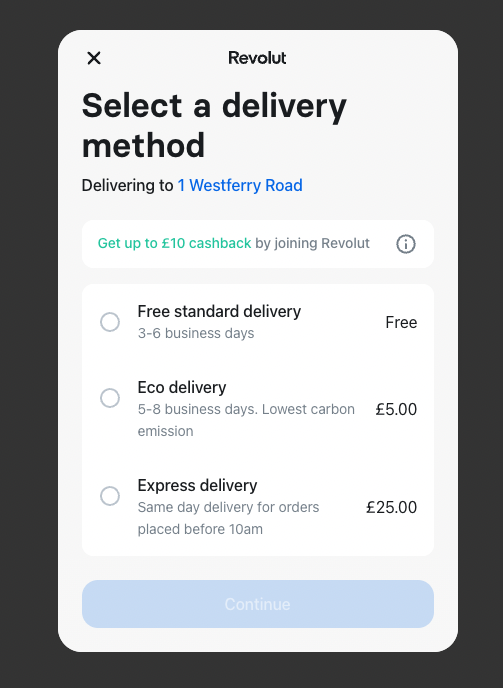
The above example has the following JSON structure:
"delivery_methods": [
{
"ref": "free_standard",
"amount": 0,
"label": "Free standard delivery",
"description": "3-6 business days",
},
{
"ref": "eco",
"amount": 500,
"label": "Eco delivery",
"description": "5-8 business days. Lowest carbon emission",
},
{
"ref": "express",
"amount": 2500,
"label": "Express delivery",
"description": "Same day delivery for orders placed before 10am",
},
]
In order to avoid malformed delivery methods to be displayed on the Revolut Pay widget, we advise to follow some best practices when adding delivery method objects to your backend:
- Make the
labelanddescriptioneasy to understand and short. - Use descriptive
refvalues to make delivery methods easier to identify. - Don't use special characters in
labelanddescription. - Don't include the delivery price in
labelanddescription. - Don't use the same
reffor multiple delivery methods. - Don't include the
refin other fields.
See the following example of a badly formatted delivery method JSON object:
"delivery_methods": [
{
"ref": "89219",
"label": "89219Shipping_method_dhl_next_day 2EUR",
"amount": 200
},
]
Performance requirements
Performance is critical since integrating your system with Revolut generates shared liability on the Revolut Pay Fast checkout user experience. To keep the risks to a minimum, here are some SLAs we expect from such address validation endpoints:
| SLA | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Connection timeout | 1 second | The maximum period of time until a connection is established. |
| Socket timeout | 5 seconds | A maximum period of inactivity between two consecutive data packets. |
Exceeding the timeout thresholds can result in Revolut terminating the connection. In this case an error is shown to the user, and they are asked to retry the checkout.
Although this error is recoverable, it leads to bad user experience.
Revolut will monitor partner performance to ensure the best experience for customers.
3. Initialize Revolut Pay widget with Fast checkout
After successfully setting up the validation webhook (Step 1. and Step 2.), you can initialize the Revolut Pay widget with Fast checkout by passing a specific option (Web and Android: requestShipping, iOS: shouldRequestShipping) in the widget configuration.
To do this on mobile platforms (iOS and Android), you can follow the standard integration process from the following steps:
Enable Fast checkout on Web
For a more detailed reference of the Revolut Pay options and button styling, see: Payments.revolutPay reference.
Pass the requestShipping: true parameter in your paymentOptions object:
const paymentOptions = {
currency: 'USD', // 3-letter currency code
totalAmount: number, // in lowest denomination e.g., cents
requestShipping: true,
createOrder: async () => {
// Call your backend here to create an order
const order = await () => {
// For more information, see: https://developer.revolut.com/docs/merchant/create-order
return yourServerSideCall()
}
return { publicId: order.token }
},
// You can put other optional parameters here
}
Congratulations! You've implemented Fast checkout for Revolut Pay!
Now you can continue following the standard integration process from: Revolut Pay - Web: 3. Mount Revolut Pay button.