Accept payments via Revolut Merchant Card Form SDK - Android
The Revolut Merchant Card Form SDK for Android allows merchants to accept card payments within their mobile applications. This guide provides step-by-step instructions for integrating a prebuilt payment form using the SDK.
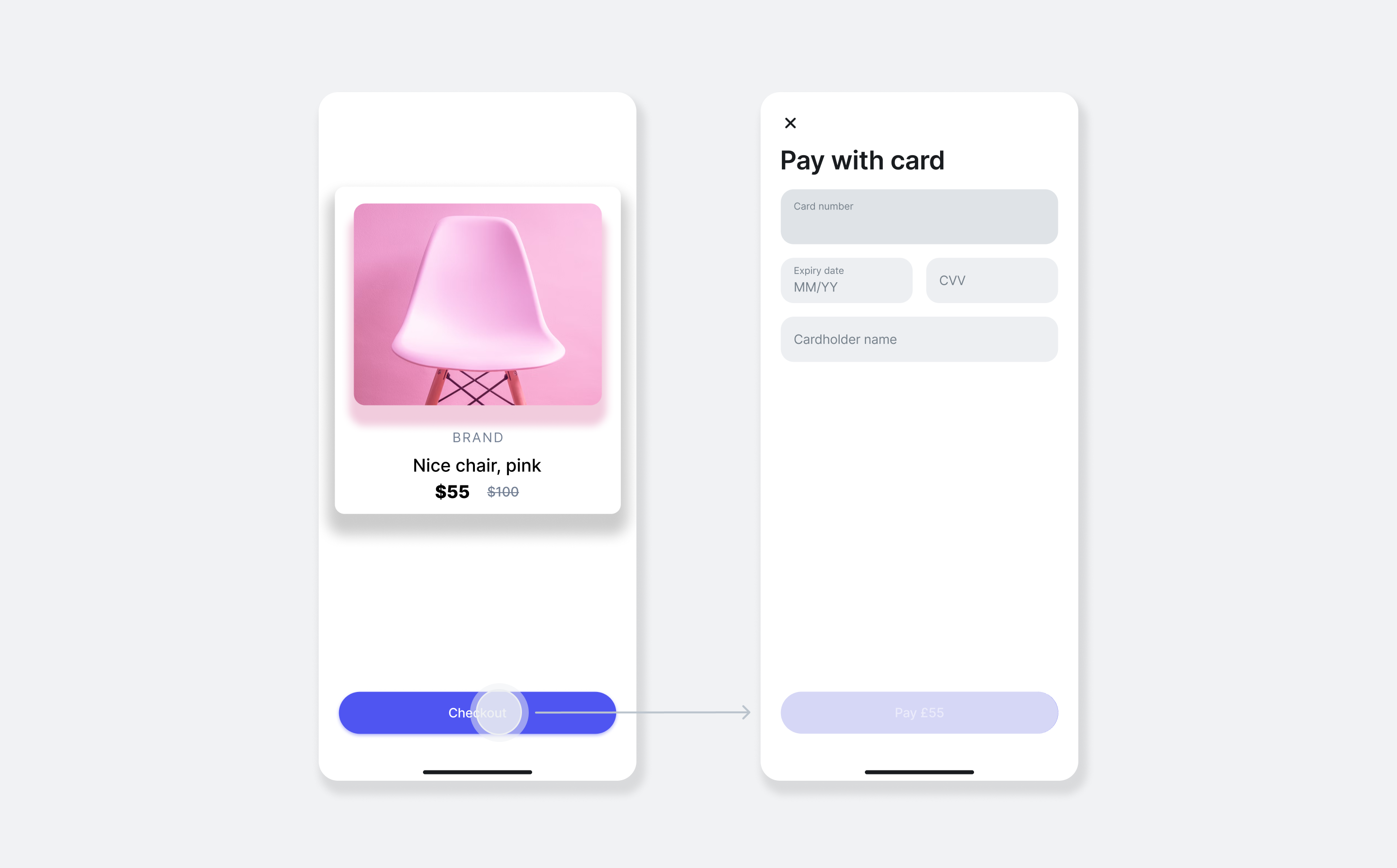
How it works
From an implementation perspective, the SDK works with the following components:
- Client-side: initialise the SDK by providing your Merchant Public API key and selecting the preferred environment to prepare for accepting payments.
- Server-side: create an order and get
token, using the Merchant API: Create an order endpoint. - Client-side: In your app, register the
CardPaymentLauncher. This component is responsible for presenting the payment UI and returning the final payment outcome to your app via a callback. - Client-side: Use the order token to call the
launchmethod on the registered launcher. This action presents the prebuilt UI activity, where the customer enters their card details and confirms the payment. - Endpoint for webhooks: optionally, you can set up an endpoint which receives webhook events from the Merchant API to track the payment lifecycle. For more information, see: Use webhooks to keep track of the payment lifecycle.
The order and payment flow is similar to all card payment solutions:
- The customer goes to the checkout page in your app, reviews their order details and decides to proceed with the payment.
- Your server uses the information from your client to create an order.
- Your client uses the SDK to initiate the payment process using the order data from the server.
- The SDK opens an activity to collect the customer's card details, handles additional actions such as 3D Secure authentication, and presents the payment result to the customer.
- Your server receives webhook notifications about each event you're subscribed to.
For more information about the order and payment lifecycle, see: Order and payment lifecycle.
Implementation overview
- Install the SDK
- Initialise the SDK
- Create an order
- Start the payment process
- Handle the payment results
Before you begin
Before you start this tutorial, ensure you have completed the following steps:
Implement the Revolut Card Payments SDK
1. Set up an endpoint for creating orders
Before the payment form can be displayed in your app, your client-side code needs a unique, single-use token that represents the customer's order. This token can only be created on your server by making a secure call to the Revolut Merchant API.
Setting up this server-side endpoint is a mandatory security requirement. Your secret API key must never be exposed in your Android application.
When a customer proceeds to checkout in your app, the app will call this endpoint. Your endpoint is then responsible for:
- Receiving the checkout details (e.g.,
amount,currency) from your client-side request. - Securely calling the Merchant API: Create an order endpoint with the checkout details.
- Receiving the order object, including the public
token, in the API response. - Returning the
tokenfrom the response to your app.
Your app will then use this token to launch the card payment activity provided by the SDK.
Below is an example of the JSON response your endpoint will receive from the Merchant API after successfully creating an order. The crucial field to extract and return to your app is the token.
{
"id": "6516e61c-d279-a454-a837-bc52ce55ed49",
"token": "0adc0e3c-ab44-4f33-bcc0-534ded7354ce",
"type": "payment",
"state": "pending",
"created_at": "2023-09-29T14:58:36.079398Z",
"updated_at": "2023-09-29T14:58:36.079398Z",
"amount": 1000,
"currency": "GBP",
"outstanding_amount": 1000,
"capture_mode": "automatic",
"checkout_url": "https://checkout.revolut.com/payment-link/0adc0e3c-ab44-4f33-bcc0-534ded7354ce",
"enforce_challenge": "automatic"
}
2. Install the SDK
- Add the
mavenCentral()repository to your project-levelbuild.gradlefile if it's not already there:
allprojects {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
}
- Add the Merchant Card Form SDK dependency to your module-level
build.gradlefile:
dependencies {
// ...
// Revolut Merchant Card Form SDK
implementation 'com.revolut.payments:merchantcardform:3.0.0'
}
- Sync your project.
3. Initialise the SDK
Before you can process payments, you need to configure the SDK with your merchant public key and the desired environment. This should be done once, typically in your application's onCreate method.
import com.revolut.payments.RevolutPaymentsSDK
RevolutPaymentsSDK.configure(
RevolutPaymentsSDK.Configuration(
environment = RevolutPaymentsSDK.Environment.PRODUCTION,
merchantPublicKey = "<merchantPublicKey>" // Your Production API Public key
)
)
4. Register the payment result launcher
Next, you need to register the CardPaymentLauncher within the Activity or Fragment that will initiate the payment. This launcher is responsible for both starting the payment UI and capturing the result in a type-safe callback.
It is crucial to register the launcher as a member variable during the initialisation of your Activity or Fragment. It must be created unconditionally, before the view is created (i.e., not within an onClick listener or after onStart()), as it hooks into the Android ActivityResultRegistry to manage the payment flow lifecycle.
The launcher's constructor receives a callback where you handle the payment outcome. Use a when statement to process all possible result types:
private val cardPaymentLauncher = CardPaymentLauncher(this) { result ->
when (result) {
is CardPaymentResult.Authorised -> {
// Payment was successful
// Update UI, navigate to a success screen, etc.
}
is CardPaymentResult.Declined -> {
// Payment was declined by the issuer
// Inform the user
}
is CardPaymentResult.Failed -> {
// A technical failure occurred during the payment process
// Inform the user or suggest retrying
}
is CardPaymentResult.Error -> {
// An error occurred, e.g., invalid parameters
// Log the error and inform the user
}
is CardPaymentResult.UserAbandonedPayment -> {
// User canceled the payment, e.g., by closing the card form screen before completing the payment
// Log the error and suggest retrying
}
}
}
This result object provides a structured way to handle the payment's final state, allowing you to update your UI and application logic accordingly.
5. Start the payment process
Once you have registered the launcher and fetched the order token from your server, you can initiate the payment process. This is done by calling the launch() method on your cardPaymentLauncher instance, typically from within an onClick listener or another user action.
The launch() method requires a PaymentParams object. You must provide the unique order token as the orderId. You can also include optional details like the customer's email and addresses to pre-fill the form, which can improve user experience and increase payment success rates.
Here's an example of how you can start the payment process:
// This call would typically be inside an onClickListener for a "Pay" button
cardPaymentLauncher.launch(
CardPaymentParams(
orderId = "<token>", // The token you fetched from your server
email = "example.customer@example.com",
billingAddress = AddressParams(
streetLine1 = "1 Canada Square",
streetLine2 = "Sample street",
city = "London",
region = "Greater London",
country = "GB",
postcode = "12345"
),
shippingAddress = null,
savePaymentMethodFor = null
)
)
| Code snippet | Explanation |
|---|---|
cardPaymentLauncher.launch | Invokes the payment flow, presenting the UI to the user. The result is delivered to the callback you registered in the previous step. |
CardPaymentParams | A data object that holds all the information required to start a card payment. |
orderId | The unique token of the order, obtained from your server. |
email | (Optional) The customer's email address. |
billingAddress | (Optional, but recommended) The customer's billing address. Providing this can increase payment acceptance rates. |
shippingAddress | (Optional) The customer's shipping address. |
savePaymentMethodFor | (Optional) Indicates whether the payment method should be saved for future use. For more information, see: Save payment methods. |
For more details about the available parameters see, Revolut Merchant Card Form SDK: Methods and parameters.
Save payment methods
The savePaymentMethodFor parameter allows you to save a customer's payment method used in the current payment session. You have the option to save a payment method either for the customer (pass UserType.CUSTOMER) or the merchant (pass UserType.MERCHANT). To learn more about customer and merchant initiated payments, see: Charge a customer's saved payment method.
If you wish to save a customer's payment details using the Revolut Merchant Card Form SDK, you need to meet one of the following requirements:
- Have a customer object with
emailand assign it to the order by providingcustomer.id - Create a new customer with
customer.emailduring order creation
6. (Optional) Set up webhooks
While your app receives the immediate result of the payment in the launcher's callback, this only confirms the initial status to the client. For a reliable and complete payment system, you should also use webhooks to receive server-to-server notifications about the order and payment lifecycle.
Webhooks are essential for a few key reasons:
- Source of truth: They provide a reliable way for your backend to track the final state of a payment, such as when it's been captured.
- Resilience: They ensure your system can handle cases where the user closes your app or loses connection after paying but before the client-side result is processed.
- Asynchronous updates: They notify you of events that happen after the initial payment, such as refunds or chargebacks.
By utilising both in-app payment result handling for immediate user feedback and webhooks for backend reconciliation, you create a robust and responsive payment processing system.
To learn how to implement webhooks, see our tutorial: Use webhooks to track order and payment lifecycle.
Example app
The SDK's public repository contains a fully functional example app designed to demonstrate how to integrate the Revolut Merchant Card Form SDK into your mobile application. This app serves as a practical reference for developers, showcasing a working implementation of the SDK's features.
Run the example application
Follow these steps to set up and run the example app:
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/revolut-mobile/revolut-payments-android.git - Open the project in Android Studio, or your preferred IDE.
- Now you can run the example app.
Implementation checklist
Before deploying your implementation to your production environment, complete the checklist below to see if everything works as expected, using Merchant API's Sandbox environment.
To test in Sandbox environment, set the base URL of your API calls to: sandbox-merchant.revolut.com/ and initialise the SDK in sandbox:
RevolutPaymentsSDK.configure(
RevolutPaymentsSDK.Configuration(
environment = RevolutPaymentsSDK.Environment.SANDBOX,
merchantPublicKey = "<merchantPublicKey>" // Your Sandbox API Public key
)
)
- Check if the card form is displayed correctly using the order
token. The order must be created in the same environment where the widget is loaded, in this case the Sandbox environment. - Make a test payment using test cards to simulate a successful payment and verify that your app correctly handles the
Authorisedresult.- (Optional) Check if the payment shows properly in your Merchant Account.
- Test for error scenarios using test cards and verify that your app correctly handles the
DeclinedandFailedresults.- (Optional) Check if the payment shows properly in your Merchant Account.
- (Optional) Setup webhook URLs for your server to receive order and payment updates.
- Check that the webhooks (for successful and failed payments) are properly received and processed.
If your implementation handles all these cases as you expect in Sandbox, it is advised you also test your implementation in production before going live. Once your implementation passes all the checks in both environments, you can safely go live with your implementation.
These checks only cover the implementation path described in this tutorial, if your application handles more features of the Merchant API, see the Merchant API: Implementation checklists.
Congratulations! You've successfully integrated the card form with the Merchant API in your app.
What's next
- Learn more about the SDK - Explore our public SDK repository for more information on integration
- Learn more about the order and payment lifecycle
- Learn more about webhooks - Check our guide about how you can track payment lifecycle with the Merchant API's webhook service
- Learn more about refunds - Check our guide about how you can refund your orders
- Learn more about saving payment methods - Check our guides about different use-cases with saved payment methods
- Learn more about order management - Explore the full capabilities of our Orders API
- Learn more about customer management - Explore the full capabilities of our Customers API